Blue GAS
The Invisible Treasure

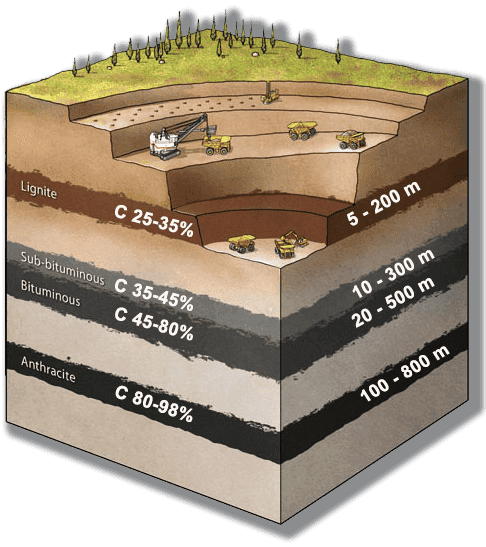
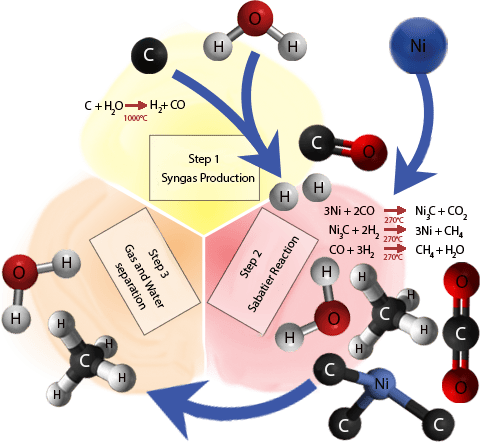
N NIMEC has developed an innovation in the technology of transforming Coal into Methane gas. Our innovation consists of electrical heating of the reactor for the production of Syngas and the reactor for the Sabatier reaction in the oxygen-free mode. The absence of oxygen has a positive effect on the course of reactions and greatly increases the yield of the final product.
I Innovations in energy technology can generate significant, quantifiable public benefits that are not reflected in the market price of energy. These benefits include cleaner air and improved public health, enhanced national security and international diplomacy, reduced risk of dangerous climate change, and protection from energy price shocks and related economic disruptions. Currently, these benefits are neither recognized nor rewarded by the free market. Having a source of electricity with aprox zero cost increases the economic feasibility of the coal to gas transformation and Net Zero production also gives the positive effect.